Software Testing is a process used to identify the correctness ,completeness, quality of the developed computer software
It also help to identify errors, gaps or missing requirement
It is done either manually or using software tools
General characteristics of strategic Testing
To perform effective testing, a software team should conduct technical reviews
Testing begins at the component level and work towards the integration of entire computer based system
Different testing techniques are appropriate at different points in time
Testing is done by developer of software and for large projects by an independent test group
Testing and debugging are different activities but debugging must be accommodated in any test strategy
Testing Strategies
Software testing is a critical element of software quality assurance and represents the ultimate review of specification, design, and code generation.
It is not unusual for a software development organization to pay between 30 and 40 percent of total project effort on testing.
The engineer creates a series of test cases that are intended to "defeat" the software that has been built.
In fact, testing is the one step in the software process that could be viewed (psychologically, at least) as destructive rather than constructive.
Type of Testing Approach
Verification and Validation approach:
Verification: "Are we building the product right?"
Verification refers to the set of activities that ensure that software correctly implements a specific function.
Validation: "Are we building the right product?
Validation refers to a different set of activities that ensure that the software that has been built is traceable to customer requirements.
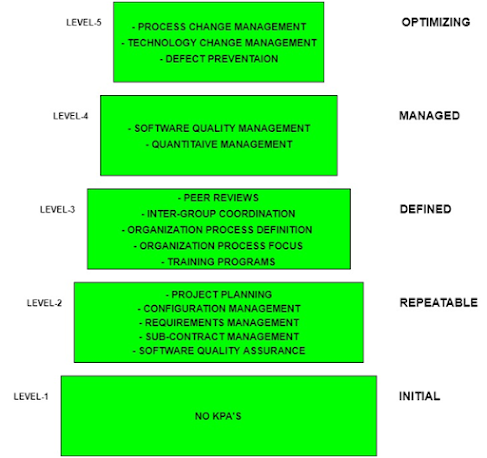
- CMM was developed by the Software Engineering Institute (SEI) at Carnegie Mellon University in 1987.
- It is not a software process model. It is a framework which is used to analyses the approach and techniques followed by any organization to develop a software product.
- It also provides guidelines to further enhance the maturity of those software products.
- It is based on profound feedback and development practices adopted by the most successful organizations worldwide.
- This model describes a strategy that should be followed by moving through 5 different levels.
- Each level of maturity shows a process capability level. All the levels except level-1 are further described by Key Process Areas (KPA’s).
- Level-1: Initial
- No KPA’s defined.
- Processes followed are adhoc and immature and are not well defined.
- Unstable environment for software development.
- No basis for predicting product quality, time for completion, etc.

No comments:
Post a Comment